Cross Selling
Cross selling is a marketing term used to describe the effort of a retailer to sell other suitable products or services in addition to a requested item with the aim of sales efficiency and higher turnover.
Function principle of cross selling
The basic aim of cross selling is to increase the sales per order. This is achieved by offering the user other products or services that might suit their needs based on the requested item. These are often products that complement the requested item for example a protective cover for a smartphone or a fitness bracelet to a nutrition guide. However, products from a completely different category can also be offered.
Sometimes, certain items are offered at prices slightly above or even below the cost price in order to cross-subsidize items with large profit margins. The success of cross selling is based on the notion that customers who have already purchased from a shop are often more willing to buy more products from the same seller. In particular, this involves the reactivation of existing customers, although cross-selling also applies to new customers. Cross selling is therefore usually part of customer relationship management.
Advantages for the seller
One of the biggest advantages for sellers are the significantly lower acquisition costs. Almost no acquisition costs are incurred for a product sold through cross selling since the customer is already there and interested. Nurturing of existing customers is also advantageous as the price sensitivity of the customers sinks. Thus, customers tend to be more willing to invest more money since they are already familiar with the quality. Other advantages of cross selling include the promotion of a product through another, improvement of customer relations, and increase in sales. In addition, cross-selling can also be used to improve the sale of older goods or make it easier to introduce new products.
Examples of cross selling
Countless examples of cross selling can be found both in retail stores and online shops. Examples include:
- At discount supermarkets, customers will find offers that change after every few days and are from different areas such as technology, clothing, toys, textiles, furniture, and much more.
- Car dealers additionally offer accident and breakdown coverage, extra winter tires, car financing services, etc. when a customer is buying a car.
- During a haircut, the hairdresser recommends a special styling mousse that the customer buys before leaving.
- Gas stations not only offer the possibility to refuel vehicles - they also sell magazines, candy, snacks, and numerous products for everyday use.
- In addition to medication, pharmacies also sell toiletries.
In some way, cross selling can also effect a change in the assortment structure such as a coffee shop starting to offer a weekly changing assortment as the main business, while coffee remains a peripheral assortment.
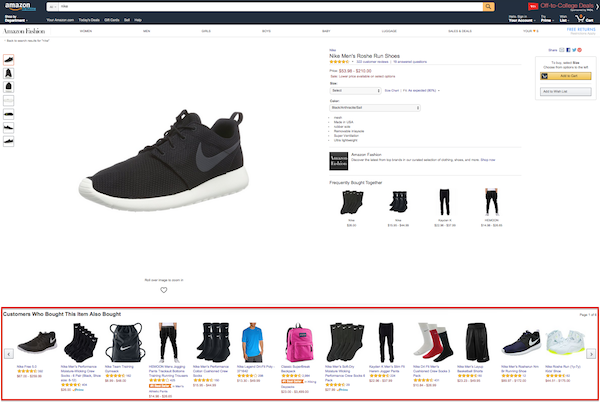
Cross selling in online shops
Cross selling is of great significance to online retailers since the spontaneous purchase of a product is only a click away and decisions to buy are often made within seconds. In online shops, cross selling is often achieved using automated tools that are integrated into the respective shop systems. There are two basic technical options that are used:
- The operator defines keywords that are associated with the product. These keywords are searched in the product database, and the corresponding products are filtered out and displayed.
- The operator keeps specific products in the master record that are to be displayed as part of the cross selling.
In practice, cross selling on the front end of a shop is mostly placed under the product or to the right of it and usually has titles such as these:
- “We also recommend the following products”
- “Customers who bought this product also bought”
- “Best-selling products in this category”
- “Accessories for this item”
- “Other products from this manufacturer”
- “Similar products”
The option to “tag” a product also exists. Here, the product is assigned associated keywords. If the tag is clicked on, other products that have the same keywords are also displayed.
Importance for search engine optimization
Cross selling is very important for online shops with regard to search engine optimization. As these naturally tend to have too little relevant content and inbound, external links to all product pages is almost impossible for large shops, indexing of all subpages of the shop is quite difficult. A comprehensive internal linking is hereby helpful. This can be achieved without too much effort through automated cross selling modules.
Extra product pages are internally linked on every product page so that, sooner or later, every item will have several internal links. As a result, the subpages can be found more quickly by search engine robots. In addition, the entire search engine optimization of the online shop is thereby improved since a healthy internal linking is an important ranking factor for the Google algorithm. Ideally, every product page should have at least ten internal links.
Significance for Online Marketing
E-commerce, in particular, relies on cross-selling. Online shops with a wide range of goods can use cross-references to point out new products, suitable articles or complementary products. With the help of Big Data or Data-Driven Marketing, cross-selling can also be optimized on the basis of valid customer data. For example, it is possible to suggest suitable products to registered users in a web shop on the basis of their previously purchased articles. Cross selling can also be integrated into email marketing. Many online retailers then send personalized emails to customers containing cross-references to other items.