Google Search
Today, “Google search” is virtually synonymous with searching for content on the web worldwide. Since being named in 1997, Google search has become a central point for many web activities. The web search is just one component of Google Inc.’s overall portfolio. However, it is the main platform to deliver text ads or PLA for its customers and thus forms the central basis for advertising revenue.
Development
Google search was designed by Larry Page and Sergey Brin in the U.S. in 1995. However, the two founders initially did not agree on the exact design. Finally, the two started the first search engine called Backrub at Stanford University, U.S.A. in 1996. The university’s own servers were used for its operation. Finally, Larry and Sergey found a separate name for their search engine: Google. They borrowed the name from the mathematical term “googol.” It denotes a 1 with 100 zeros. A number that approximately describes the huge amount of web content that a search engine needs to process.
Back in 1998, Google search is recorded for the first time in the top 100 websites of PC Magazine. Up until 1999, the Google team consisted of just eight employees. In August of the same year, they moved into their first offices in Mountain View, California.
In 2000, Google search is available in 15 different language versions and the search engine index is the largest in the world with a billion URLs. Other notable steps are the start of the advertising network Google AdWords and the introduction of the Google Toolbar. Through AdWords, the Group soon had enough funds available to improve Google search even further. Using the toolbar, the search function is even more widespread. Moreover, the cooperation with Yahoo! ensures that Google search becomes standard in all Yahoo! products.
2001 is a big year for Google, because it was the year when the image search was started and Eric Schmidt joins the executive team. The first location outside the US is opened in Tokyo at the same time. The search index has now grown to over three billion URLs.
The growth of Google search index is listed here briefly to demonstrate its rapid growth:
- January 1998 (business creation) 25,000,000 pages indexed
- August 2000 1,060,000,000 pages indexed
- January 2002 2,073,000,000 pages indexed
- February 2003 3,083,000,000 pages indexed
- September 2004 4,285,000,000 pages indexed
- November 2004 8,058,044,651 pages indexed
The group no longer publishes the exact number of indexed documents. The search engine is even able to identify new websites. Therefore, registration is no longer required.
A year later, in 2002, Google search can be used in 72 different languages. Typical of Google, its employees prove their sense of humor not just on April 1, by releasing a language version in Klingon. 2002 was also the year when Google search was extended with Google News as a separate search and Google Shopping was added as well.
In 2003, the verb “to google” is publicly mentioned for the first time in the US. That same year, Google Search is now available in over 150 countries. Since 2006, the verb “to google” also has its own entry in the Oxford English Dictionary.
The subsequent history of the Google search shows how the search engine company gradually growing and potentially taking over additional areas. The most important extensions of the Google search with corresponding years are listed below in brief:
- 2004: Google Local, orkut, Google Desktop Search, Google Scholar, Google Books
- 2005: Google Maps, mobile web search, Google blog search, Google Transit, Google Analytics
- 2006: Google Finance, Google News for mobile, Google Trends; Google Patents, Google Checkout
- 2008: Google Chrome browser with Google search as the default via the central search bar
- 2009: Rich Snippets in the SERPs
- 2010: Google Places, Google Voice, Google Instant
- 2011: Google Offers
The result is that Google search no longer simply represents today only a simple web search, but a complex search engine that can be used across devices specifically when searching for documents or content. In addition, Google uses its vast supply of data to further advance the universal search. The fact that the Google Search is geared for more complex queries, for example, is proven by the expansion of the Knowledge Graph in the course of the Hummingbird update.
Search engines, which do not store IP address or user data are DuckDuckGo and Ixquick.
How it works
Google search is based on a separate index similar to other web search engines. A bot crawls the world wide web and collects in his quest content and URLs which are then stored on a server. Google uses several indexes to store the contents of its vertical search functions. Thus there is, for example, a separate index for images, books, or mobile websites.
When you launch a search query on Google, the algorithms compare it to the stored data in the search engine index and deliver the data as search results sorted by relevance.
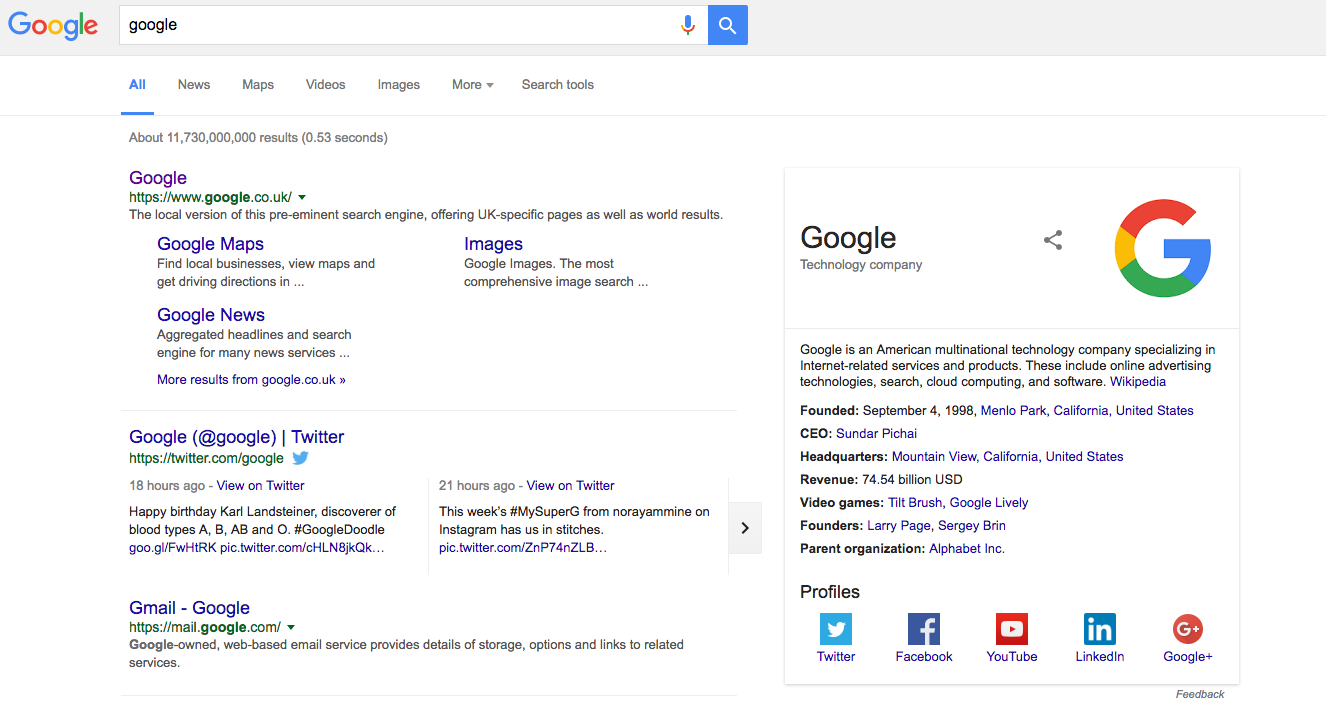
The search results
Nowadays the list of results or SERPs of a Google search are usually multi-layered. The individual search results, called snippets, consist of the following:
- Title in blue (if that page was already clicked, it appears in purple): usually the meta page title of the website or a title stored in a directory such as DMOZ will be shown here. Google can customize the display of the title, if necessary, to achieve an even higher results relevance
- Link in green: Google directs to the link target
- Description in gray: either meta description stored by the webmaster is used or a compilation of web content from the landing page
- Links to other Google features in blue
- Directly below the search bar, you have the option to use Google’s special search functions
- The total number of results and the time required for the search are displayed above the results.
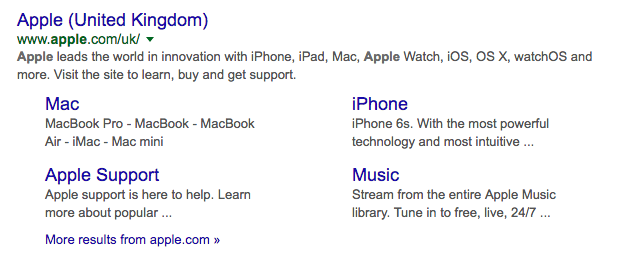
Here is an example of a more complex snippet for the search “Apple:”
The “sitelinks” are especially recognizable here. These are deep links that are automatically integrated by Google in the search results list, so that you can get directly to the other content.
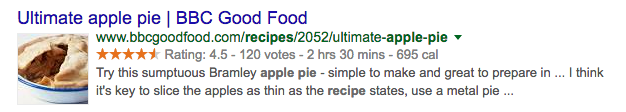
Another example illustrates the expansion of the snippet with additional information in the form of a “rich snippets:”
The Google Doodle
The Google Doodle is an adaptation of the Google logo on the Google search homepage. The Google Doodle is often used to honor celebrities or represent holidays such as Halloween. These changing doodles are mostly well received by the Internet community. In many cases, these doodles are also interactive.
Google vertical search
Google search is more than just a simple web search. The user benefits from various vertical search functions that can be integrated directly in the SERPs for related queries.
- Google Shopping: this is a price comparison portal, which is fed by the Merchant Center and bookings through Google AdWords
- Google Images: This is a separate index for images that can be searched based on your own uploaded images or using URLs
- Blog search: This allows you to search for content that is published on blogs. However, the results are not always genuine blog posts
- Location search: With Google Maps or directly from the search bar, Google search can also be used to search for locations or stores
- Google Books: Up to the present, Google has been scanning millions of books and made them searchable for the search engine. Many scientific books can be searched with the help of Google. The service, however, is quite controversial due to copyrights issues.
- Google Scholar: This is a search function for the scientific field. Articles, theses or monographs can be browsed using this search function
- Google Videos: Google’s own video search includes results from ordinary websites as well as search results from YouTube or other video platforms
- Google News: using the News-Search, users can search the web for current topics
- Google Patents: Google has indexed thousands of patents and made them searchable for users worldwide
- Google Flights: Since its acquisition of the provider ITA, Google has its own flight search since 2011
- Google Discussion: With this separate vertical search, you can specifically search through forums such as Google Groups and blog comments
- Google Play: central portal for apps that can be installed on android-based devices
Important search engine updates
Since Google is the market leader in the field of web search in most countries of the world, updates to the search engine algorithm are particularly closely watched by SEOs. Google changes its algorithms periodically. Usually, these optimizations are geared to tackle spam.
The following updates are among the most prominent in the history of Google search:
- Panda: This is a filter of the Google search which penalizes poor quality sites
- Penguin: With the Penguin update, Google combats webspam more intensively
- Hummingbird: With it Google was able to answer more complex queries
- Cassandra: This update mainly addressed hidden content
- Fritz: This algorithm change was to put an end to the Google Dance by carrying out updates in several stages
- Caffeine: This change to the Google search infrastructure was to ensure that more than half of the search results would be more current. The later Freshness update provided for even more current results on specific topics where this is relevant.
- Jagger: This update was primarily targeting link farms and sites that offer paid links
- Florida: This update primarily fought spam techniques like keyword stuffing
- Allegra: Penalizing of sites with suspicious links
Search options
The search results of Google search can be filtered based on various criteria such as:
- Results from a particular country
- Results in a certain language
- Release date
- Literal search
- Results nearby
- Results from the private search history
In addition, the Google search offers even more features that have become widespread for search services on the web:
- Google Instant: Google suggests other applicable search terms as you type which you can click. In the background, the result lists are always updated based on the most relevant terms.
- Google Suggest: Search terms will be automatically completed when entered into the search bar.
Search operators
Complex queries can be performed with Google search. The search bar can, for example, be used as a calculator or currency converter. In addition, the search results can be limited using operators. A popular operator for SEOs is a search site, by means of which the indexed pages of a website can be queried. Google Help has released a list of usable search operators.
Google Custom Search
Google offers its search function to webmasters who want to make their website searchable using Google. The advantage of this method is that users are already familiar with the layout of the Google search and give it great confidence. The Google Custom Search service is a paid service and available starting at $100 per year. The city of Boston uses the custom search at Boston.com.
Voice-activated search function
Since 2011, you can use the voice-activated search function in the Chrome web browser. Earlier, Google had already equipped its Android operating system with a voice control. Thus, the company responds to the voice control “Siri,” which is used in Apple products. Voice-activated search has the advantage that you can get your result without typing or tapping. Google itself can benefit from the voice search to optimize its voice control in general and the translation service Google Translate. The company’s goal is to expand speech recognition to a point where telephone conversations can be automatically translated between people who do not speak a common language.
Modification of search results
In order to get indexed for Google search, you previously had to register your website with Google. This is still possible, but usually the bots discover new content by themselves, by following existing links.
However, sometimes the opposite might be the case and you want to remove your website from the index. You can do so using the Google Search Console. The following aspects can be handled through these:
- Request for deletion of web pages from the Google index
- Deletion of sitelinks
- Deletion of caches
More information on this subject can be found in Google’s blog post.
SEOs and webmasters have the option to influence the display of search results in the SERP by working with “markups” which are used as part of rich snippet optimization. More information can be found on www.schema.org.
Possible reasons why Google search is so successful
Google search has been praised already very early for its speed and the precision of the search result lists. The simplicity of the search function which needs no further explanation is obviously also appreciated by users. Moreover, Google has succeeded early on to integrate its search function in all kinds of devices and software such as browsers as a default. Even in the competitive browser “Internet Explorer,” Google was used as a default search engine for a long time.
Today, Google has probably the world’s largest search engine index and can therefore provide its users with the best possible results. The constant adaptation to the needs of web users and cross-platform expertise that Google was able to acquire through the acquisition of Motorola in 2012, put the competition in the search engine market under massive pressure. Only Yandex in Russia and Baidu can currently defy Google in terms of web search in a limited regional scope.
Criticism of Google search
The fact that Google search has become a central entry tool for all your web activity and research is not always met with consent. One of the main criticisms is that Google has excessive influence on the search results by evaluating the index and therefore it no longer represents an objective search.
This criticism is reinforced by the fact that Google delivers personalized search results and results based on the profile for logged in users or via the activated web history.
In particular, the personalized search can prevent specific websites from appearing at the top of the rankings in the SERPs, because the evaluation of the search history of the user determines this by means of algorithms. Google itself usually sees no need to act on this, because in the eyes of the search engine company, the highest relevance of the results is what matters and that the users get the results they need. Web history and search history are supposed to assist with this.
In addition to the criticism of the lack of objectivity of the search function, the increasing Google search functionality is being critically viewed in SEO circles. Because features such as the Knowledge Graph or the integration of results from the vertical search and the expansion of advertising space with product listing ads or other forms of advertising are decreasing the space for the organic search results. In extreme cases, only three places remain for organic search results for certain search queries. And these results are barely visible just above the scroll line. This means for search engine optimization that only the top 3 results will count. Phenomena such as attention to web hits at number 10 of the first page are no longer so relevant.
Look at the future
The future of web search is discussed over and over again. The Google search plays a central role. One of the crucial aspects of this search will be semantic search, making it possible to answer complex queries. The Hummingbird update provides preliminary evidence in this regard. Marcus Tandler explained what the future of web search may look like in a lecture “The Future of Search” at the Tedex Munich.
Web Links